Diesel fuel is an essential energy source that powers a vast array of vehicles and machinery across the globe. From trucks and buses to ships and industrial equipment, diesel plays a crucial role in the world’s economy. But have you ever wondered where diesel fuel is refined? Understanding the refining process and the locations where it takes place can offer valuable insights into the energy industry. This article delves into the intricacies of diesel fuel refining, exploring the global network of refineries that produce this vital fuel.
Introduction to Diesel Fuel Refining
Diesel fuel is derived from crude oil, a complex mixture of hydrocarbons found in underground reservoirs. The process of transforming crude oil into diesel fuel involves several refining stages that separate and convert different components of the crude oil into usable products. Diesel refining is a critical part of the petroleum industry, providing the fuel needed for transportation, agriculture, and industry.
What is Diesel Fuel?
Diesel fuel is a type of distillate fuel obtained from crude oil through the refining process. It is known for its high energy content and efficiency, making it ideal for heavy-duty engines. Diesel engines are preferred in many applications because they offer better fuel economy and longer engine life compared to gasoline engines.
Importance of Refining
Refining is essential because crude oil in its natural state is not usable as fuel. The refining process breaks down crude oil into different fractions, each of which has specific uses. Diesel is one of these fractions, and its quality and properties are determined by the refining process.
Global Locations of Diesel Fuel Refining
The refining of diesel fuel takes place in large facilities known as refineries. These refineries are strategically located around the world, often near major crude oil-producing regions or close to large markets where the fuel is needed. Let’s explore some of the key regions where diesel fuel is refined.
1. North America
North America is home to some of the largest and most advanced refineries in the world. The United States, in particular, has a vast network of refineries located primarily along the Gulf Coast in states like Texas and Louisiana. These refineries are well-positioned to access crude oil from both domestic sources and imports.
The U.S. Gulf Coast: The Gulf Coast is the epicenter of the U.S. refining industry. This region’s refineries are capable of processing various types of crude oil, including heavy and sour crudes. The proximity to major ports allows for the easy export of refined diesel to international markets.
Canada’s Refineries: Canada also has significant refining capacity, particularly in Alberta, where the oil sands are located. Refineries in this region process crude oil extracted from the oil sands, converting it into diesel and other products.
2. Europe
Europe has a well-established refining industry, with refineries spread across the continent. Countries like Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom are key players in diesel fuel production.
Germany’s Refining Industry: Germany is one of Europe’s largest producers of diesel fuel. The country’s refineries are highly advanced, focusing on producing high-quality diesel that meets stringent environmental standards.
The Netherlands and Rotterdam Port: The Netherlands is home to the Port of Rotterdam, one of the world’s largest and busiest ports. The refineries in this region are strategically located to access crude oil from the North Sea and other regions. Rotterdam’s refineries are crucial for supplying diesel to European markets.
3. Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region has seen rapid growth in refining capacity, driven by increasing demand for diesel fuel in countries like China, India, and Japan.
China’s Expanding Refining Sector: China has invested heavily in its refining industry, with numerous refineries scattered across the country. The demand for diesel in China is significant, driven by the country’s industrial and transportation sectors.
India’s Reliance on Refining: India is another major player in the refining industry, with several large refineries that produce diesel for both domestic use and export. The country’s refining sector is a vital part of its energy infrastructure.
4. Middle East
The Middle East is a key region for diesel fuel refining, thanks to its vast crude oil reserves. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates are major producers of diesel fuel.
Saudi Arabia’s Refineries: Saudi Arabia has some of the largest refineries in the world, capable of processing millions of barrels of crude oil per day. The refineries in this region are equipped to produce high-quality diesel fuel for export.
Kuwait and UAE’s Refining Capabilities: Both Kuwait and the UAE have significant refining capacity, with refineries located near major oil fields. These refineries produce diesel that is exported to markets around the world.
5. Latin America
Latin America also plays a role in diesel fuel refining, with key refineries located in countries like Brazil, Venezuela, and Mexico.
Brazil’s Refining Industry: Brazil is one of the largest refining countries in Latin America. Its refineries are spread across the country, producing diesel for domestic consumption and export.
Venezuela’s Oil Refining Challenges: Venezuela, despite having vast oil reserves, faces challenges in its refining sector. The country’s refineries have been affected by political and economic instability, impacting diesel production.
See also: Will Diesel Fuel Freeze? [Revealed]
The Refining Process
The process of refining diesel fuel involves several key steps, each of which plays a crucial role in producing high-quality fuel. Let’s take a closer look at the refining process.
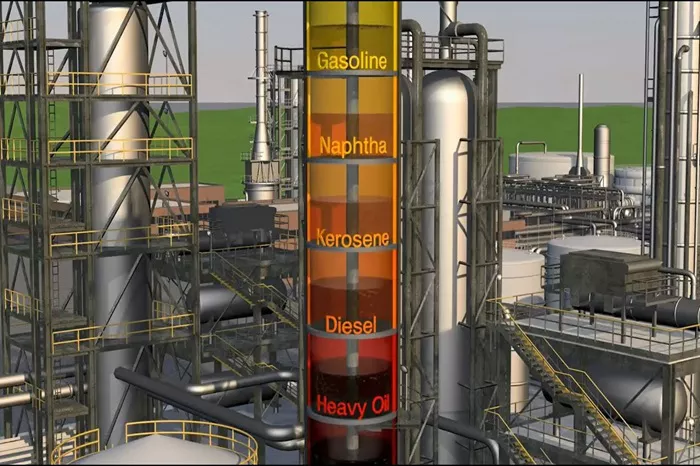
1. Distillation
The first step in refining diesel fuel is distillation. Crude oil is heated in a distillation tower, causing it to vaporize. As the vapor rises through the tower, it cools and condenses into different fractions based on their boiling points. Diesel fuel is one of these fractions, collected at a specific point in the tower.
2. Hydrotreating
After distillation, the diesel fraction undergoes hydrotreating, a process that removes impurities such as sulfur. This step is crucial for producing clean diesel that meets environmental standards.
3. Catalytic Cracking
In some cases, diesel fuel may undergo catalytic cracking, a process that breaks down larger hydrocarbon molecules into smaller ones. This step helps increase the yield of diesel fuel from crude oil.
4. Blending
Finally, the refined diesel is blended with additives to improve its performance and stability. These additives can enhance the fuel’s cetane rating, lubricity, and cold flow properties, ensuring that it performs well in various conditions.
Environmental Considerations
The refining of diesel fuel has significant environmental implications. Refineries are major sources of greenhouse gas emissions and other pollutants. However, advancements in refining technology have helped reduce the environmental impact of diesel production.
1. Emission Controls
Modern refineries are equipped with advanced emission control technologies that help reduce the release of harmful pollutants. These technologies include flue gas desulfurization, selective catalytic reduction, and carbon capture and storage.
2. Cleaner Diesel Production
The demand for cleaner diesel has led to the development of ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD). ULSD has significantly lower sulfur content than traditional diesel, reducing its environmental impact.
3. Renewable Diesel
In addition to traditional diesel refining, there is growing interest in renewable diesel, produced from biomass sources such as vegetable oils and animal fats. Renewable diesel offers a more sustainable alternative to conventional diesel fuel.
Conclusion
Diesel fuel refining is a complex and essential process that takes place in refineries around the world. From the U.S. Gulf Coast to the Middle East, refineries are strategically located to meet global demand for diesel fuel. The refining process involves several key steps, including distillation, hydrotreating, and blending, each of which plays a crucial role in producing high-quality diesel. As the world continues to seek cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, the refining industry must adapt to meet these challenges while continuing to provide the fuel that powers the global economy.
Related topic: