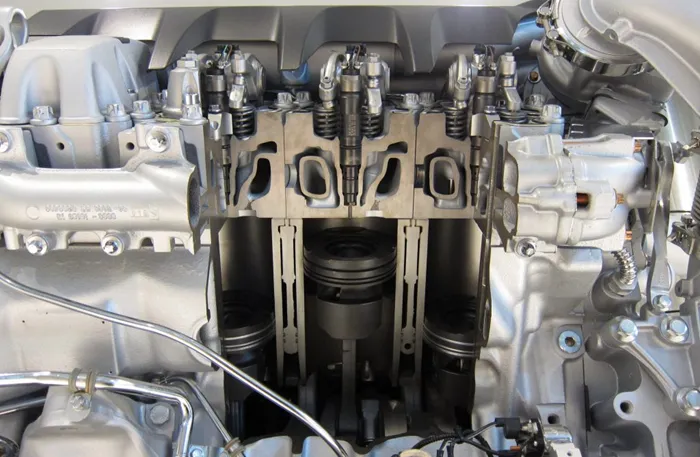
In a diesel engine, the fuel injector plays a vital role in delivering fuel into the combustion chamber. It ensures that the fuel is supplied in the right quantity and at the right time for efficient combustion. This precision contributes to the engine’s performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
Function of Diesel Fuel Injectors
Fuel Delivery
The fuel injector receives diesel fuel from the fuel pump, which pressurizes it to high levels, often exceeding 30,000 psi. This high pressure is essential for atomizing the fuel into a fine mist, promoting effective mixing with air in the combustion chamber and ensuring complete combustion.
Fuel Injection Timing
Precise timing of fuel injection is crucial for optimal engine performance. The injector must deliver fuel at the exact moment when the piston is in the correct position during the compression stroke. Modern diesel engines utilize electronic control units (ECUs) to manage injection timing with high precision, enhancing performance and reducing emissions.
Atomization
Once pressurized, the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber through a nozzle with tiny openings. The high pressure forces the fuel through these openings, breaking it into a fine mist. This process, known as atomization, ensures thorough mixing with air, facilitating efficient combustion.
Combustion
In the combustion chamber, the atomized fuel mixes with compressed air and ignites due to the high temperature generated by compression. This ignition creates a powerful explosion that drives the piston down, generating the mechanical power needed to move the vehicle.
Types of Diesel Fuel Injectors
Mechanical Injectors
Mechanical injectors, found in older diesel engines, rely on the engine’s camshaft to operate. These injectors are relatively simple and durable but lack the precision of modern systems.
Electronic Injectors
Modern diesel engines use electronic injectors controlled by the ECU. These injectors offer precise control over injection timing and fuel quantity, improving performance, efficiency, and emissions.
Common Rail Injectors
Common rail injectors are part of a high-pressure fuel system where fuel is stored in a common rail and delivered to each injector. This system allows for multiple injections per cycle, enhancing performance and reducing noise and emissions.
Piezoelectric Injectors
Piezoelectric injectors use piezoelectric elements to control the injector’s operation. These elements change shape when electrically charged, enabling rapid and precise movement of the injector needle. This design allows for multiple injections per cycle, improving combustion efficiency and reducing emissions.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular Cleaning
Over time, injectors can become clogged with carbon deposits and other contaminants, leading to reduced performance. Regular cleaning, using fuel additives or professional services, helps maintain optimal injector function.
Fuel Quality
Using high-quality diesel fuel prevents the buildup of deposits and contaminants in the injectors. Purchasing fuel from reputable suppliers and considering additives can improve fuel quality.
Timely Replacement
Injectors can wear out over time, leading to poor performance and increased fuel consumption. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for injector replacement intervals ensures the engine runs smoothly.
Monitoring Performance
Monitoring engine performance indicators, such as fuel efficiency and power output, helps detect injector issues early. Any significant changes could indicate injector problems that need attention.
Troubleshooting Common Injector Issues
Common injector issues include hard starting, rough idling, and excessive smoke. Inspecting injectors for leaks, clogs, or electrical issues and addressing them promptly can prevent further engine problems.
Conclusion
Diesel fuel injectors are essential for delivering fuel into the combustion chamber in a precise and controlled manner. Understanding their function and maintenance is crucial for optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and longevity.
Related Topics: